- 19 Nov 2024
- 7 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Querying Instances
- Updated on 19 Nov 2024
- 7 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Executing transaction queries for data tracking is different for Custom Logging and Data Queries BAM types.
Custom Logging
Query data available for execution will be sourced from the SQL database set up for the BAM environment.
Consider the following scenario: A user has their solution up and running and uses Turbo360 Business Activity Monitoring to manage it. Corporate users frequently ask the billion-dollar question, "Where is the message?" A Query search is a solution to this issue.
Users can easily search for transactions on the Tracking section using the Business Activity Monitoring search language query provided. A business process is associated with a Business Application. The process has transactions flowing through it, and tracked properties are enabled.
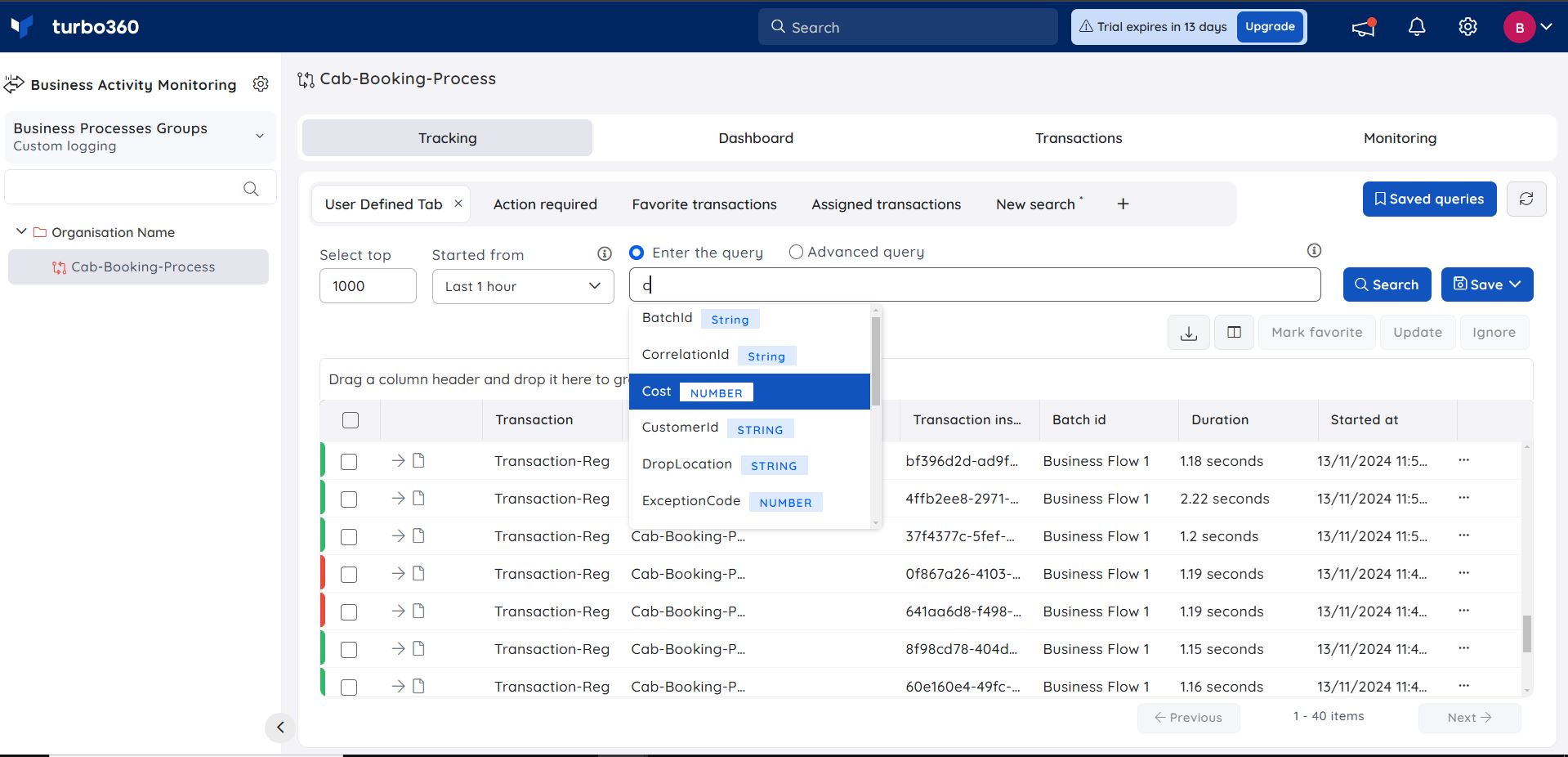
Assume a user has some transactions and wants to search for a specific transaction; if the user types Transaction in the Search field, the user will get IntelliSense for it.
- Users can see the completed transactions entered in the search bar once they have entered the entire query and hit search.
The tracking search results will display the latest 1000 records of transaction instances for a given business process, which are organized in descending order based on the transaction instance's start time.
The number of records displayed per page can also be customized by entering the required value in the Select Top field. Clicking the Next button in the footer displays the next set of records, if available.
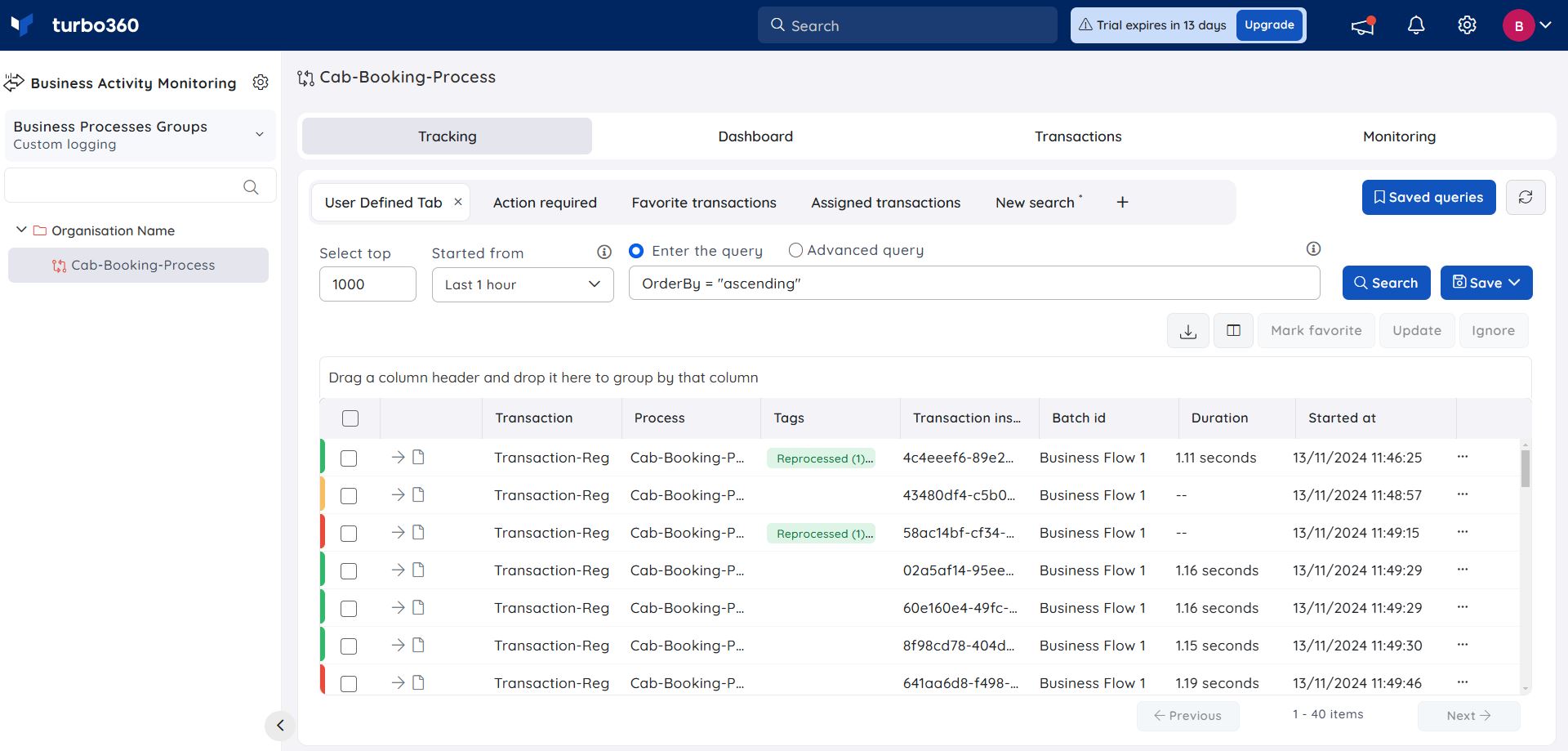
A query search can be performed to display the latest (or) oldest records. For example, Order by = "ascending" query fetches all the oldest records first with respect to the number of records to be displayed.
Query language
Turbo360 features a Domain-Specific Language that users can use to search for activities. All the properties set up in the business process configuration page will be searchable, and users will be notified if any query elements are incorrect.
Following are some examples of queries:
Searching for an exact match
- SenderId = "Milford"
Searching with wildcard characters
- SenderId like "%Milford%"
- SenderId not like "%Milford%"
- SenderId like "%Mi_ford%"
Searching for integer property using comparison operators
- Price > 10
Searching for null values
- Status = NULL
Searching using combinations
- SenderId = "Milford" and Price > 10
Searching using groupings
- (SenderId="Milford" and Price > 10) or (ReceiverId="Miles" and Price<10)
Searching for assigned transactions
- AssignedTo = "me"
- AssignedTo = "mail_id"
These two queries support only in the Assigned Transactions tab.
Search using status and duration
- Status = "inprogress" and TransactionDuration > "1min"
Free text search
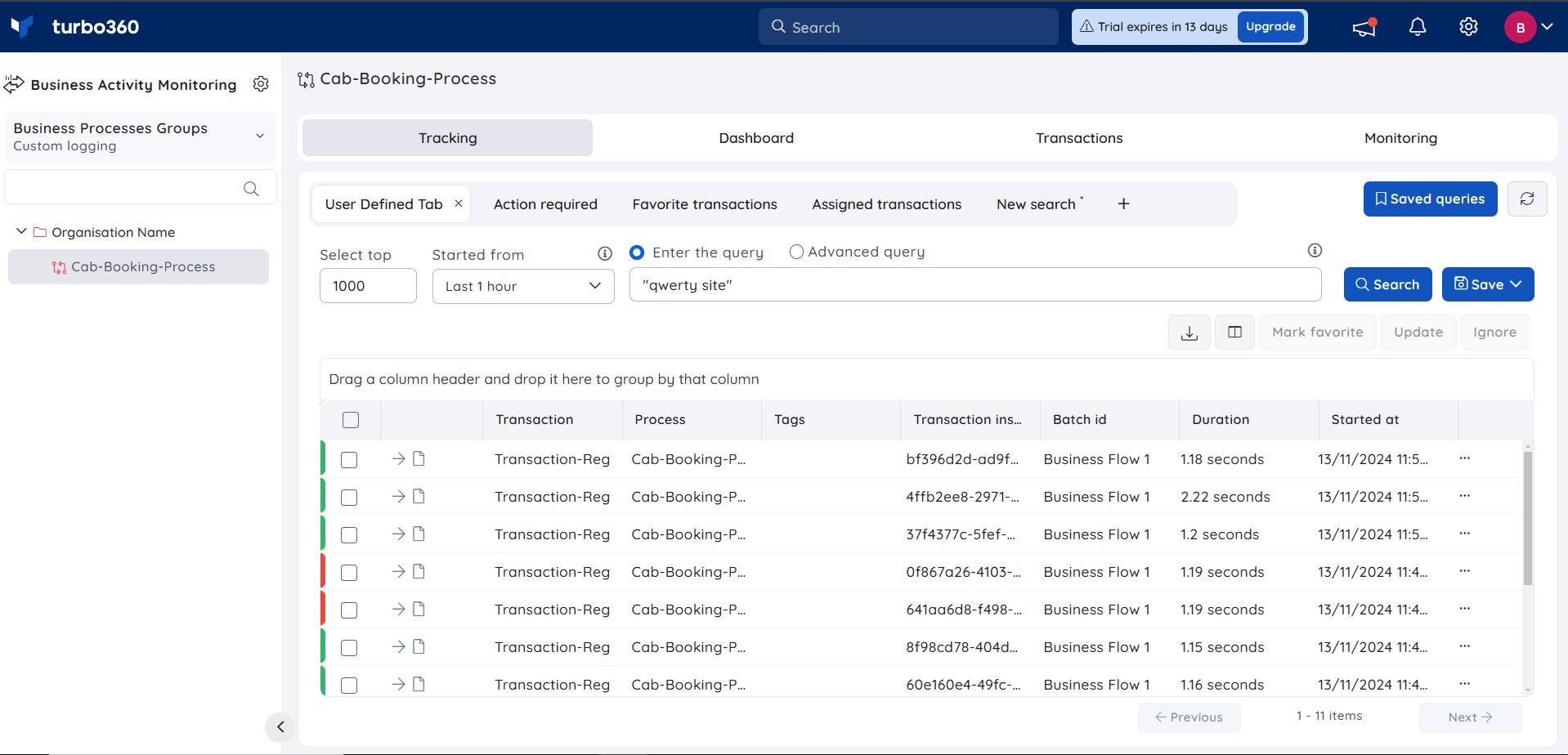
Users can efficiently perform query searches by simply entering a value in the query field rather than providing the entire query.
The input value for Integer data types must be entered without double quotes (").
The query value for String data types must be enclosed in double quotations(").
The query data for Date type can be generated by simply entering "getdate(MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss)" in the query field.
Search based on the elapsed time
Turbo360 Business Activity Monitoring also supports the option to query the transaction instances based on the elapsed time of the transaction.
The elapsed time is shown in the Duration column on the tracking page.
This search query can also be used in Query monitors to monitor the Duration of the transaction.
Following are some queries based on elapsed time:
TransactionDuration < "1 ms"
TransactionDuration < "1 s"
TransactionDuration < "1 min"
TransactionDuration < "1 hr"
TransactionDuration < "1 d"
Search based on exceptions
Users can query transaction instances based on exception code and exception message in Turbo360 Business Activity Monitoring.
Users can use this search query to track transaction instances with exceptions.
Pre-requisites
Before beginning this query search, make sure to meet the following requirements:
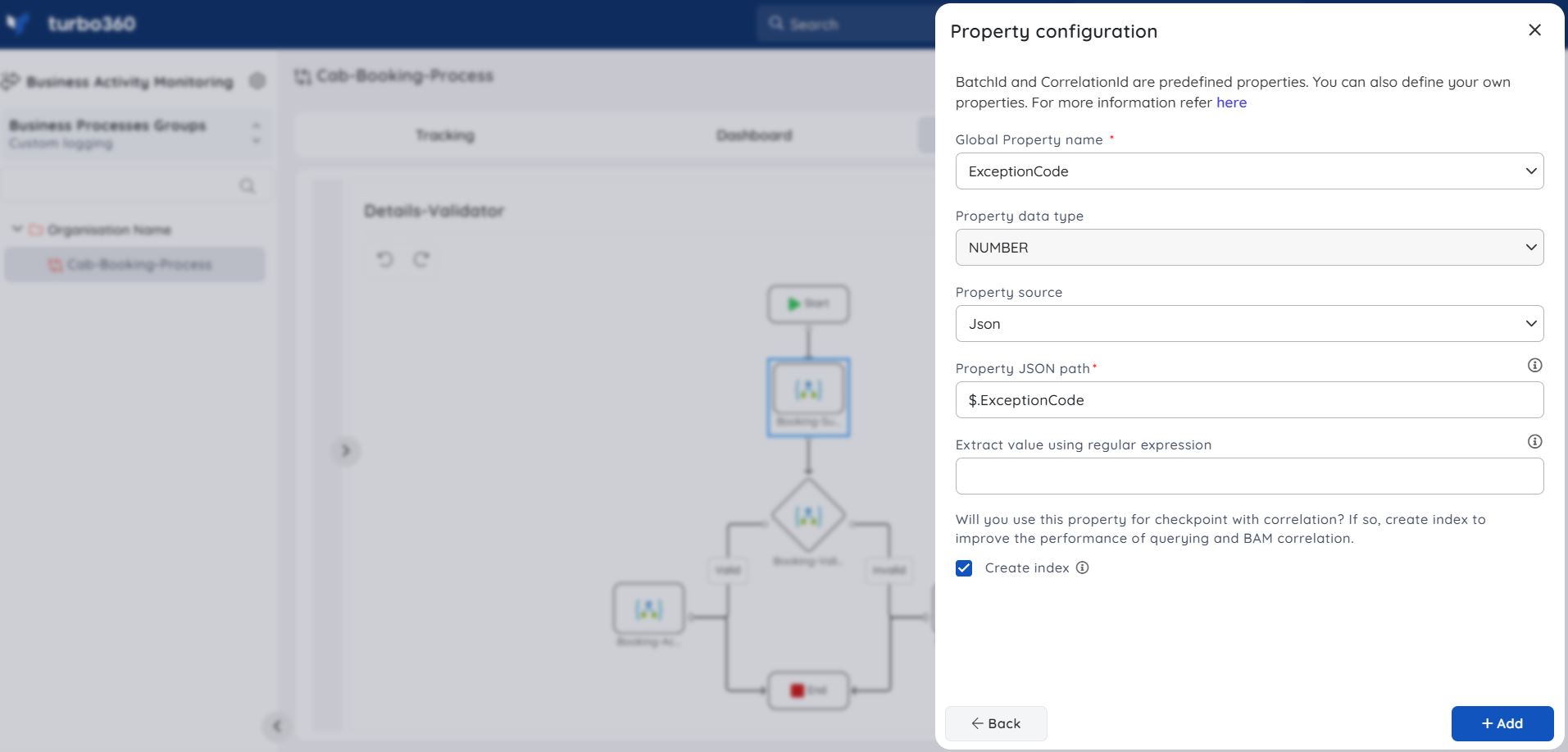
1. Creating global properties for exceptioncode and exceptionmessage
- Users must define global properties for exceptioncode and exceptionmessage, with data types NUMBER and STRING, respectively.
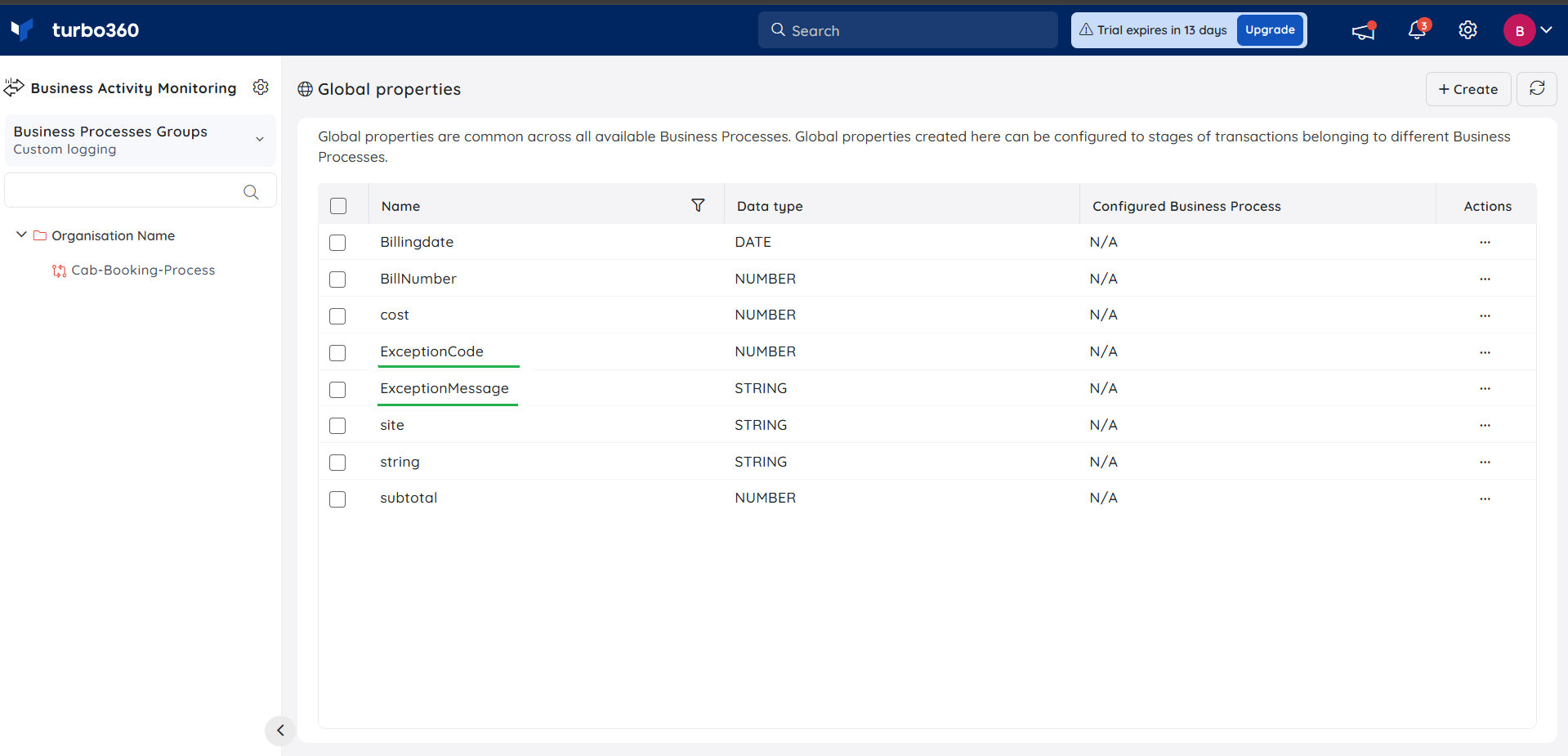
Refer to this article for creating global properties.
2. Configuring global properties to a Stage in the desired Transaction
- The next step is to assign the newly created global properties to a stage in the desired transaction.
Query Search
Following are some queries based on exceptions:
exceptioncode = 100
exceptionmessage = "exception100"
exceptionmessage like "%exce%"
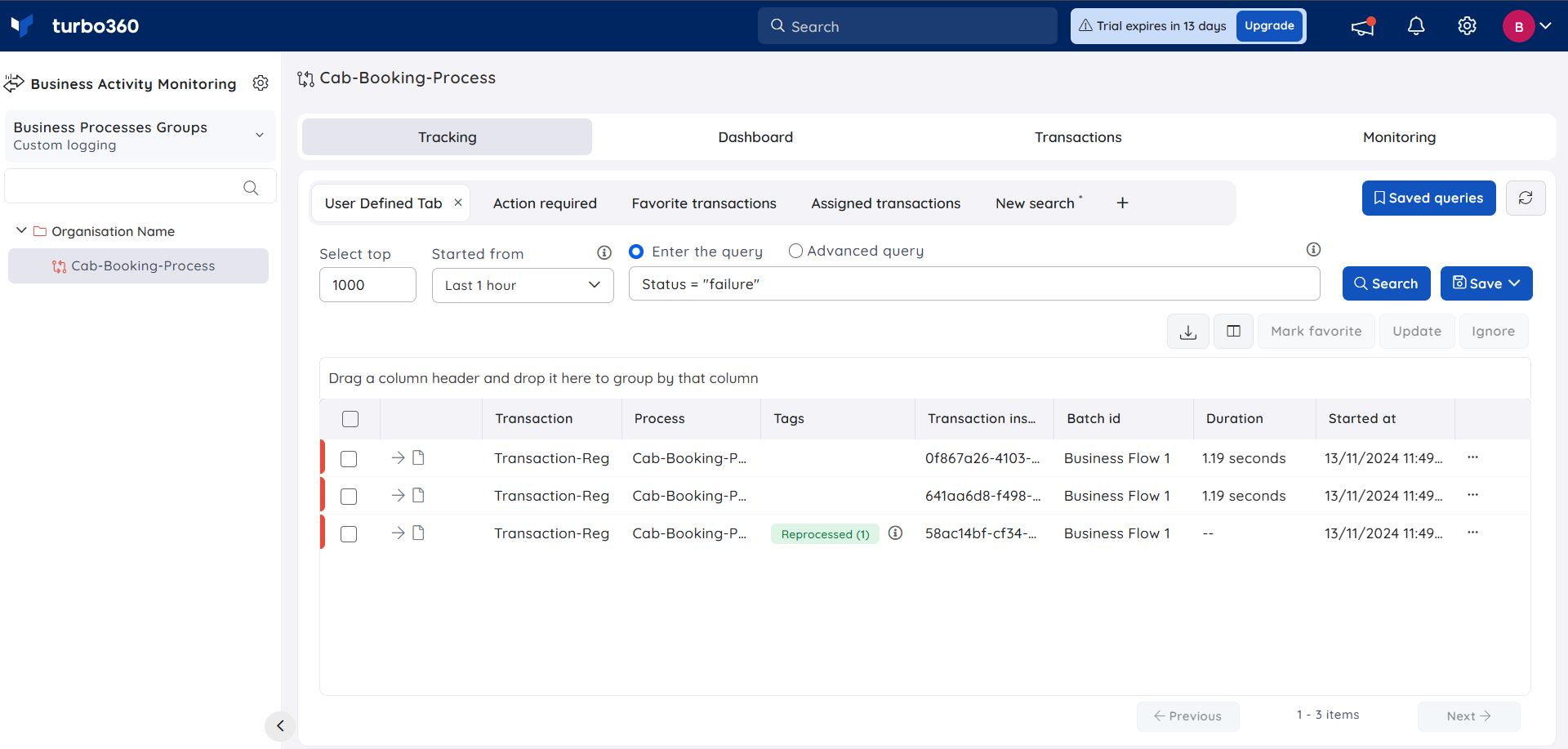
Search based on tags
Users can also query transaction instances based on the tags attached to them.
Ignored and Reprocessed are two of the available tags.
The following are some queries based on tags:
Reprocessed = "true"
Ignored = "false"
Reprocessed = "false"
Ignored = "true"
Search based on date properties
Turbo360 allows users to search the properties of the Data Type Date in a much easier way. Such properties can be searched by using the getDate() function in the Search Query.
For example, if a user wants to raise the invoices raised before 04/25/2020 09:24:26, then the user can use the Search Query.
MM/DD/YYYY HH:mm: ss
RaisedAt <= "getdate(04/25/2020 09:24:26)"
RaisedAt is the tracked property's name, and the property's data type is Date.
If there is a need to search the tracked data based on the current time, we can use the following Search Query.
RaisedAt <= "currenttime()"
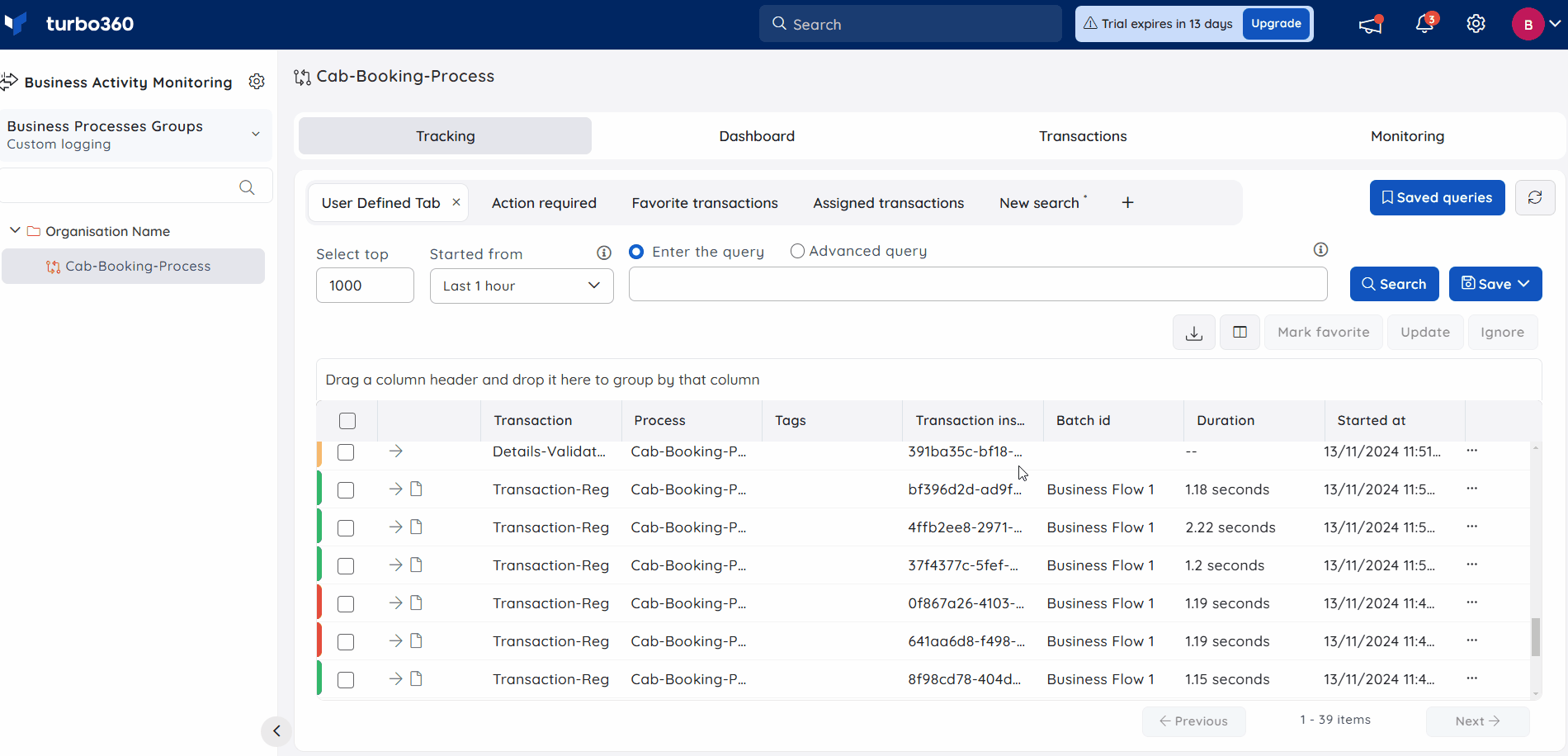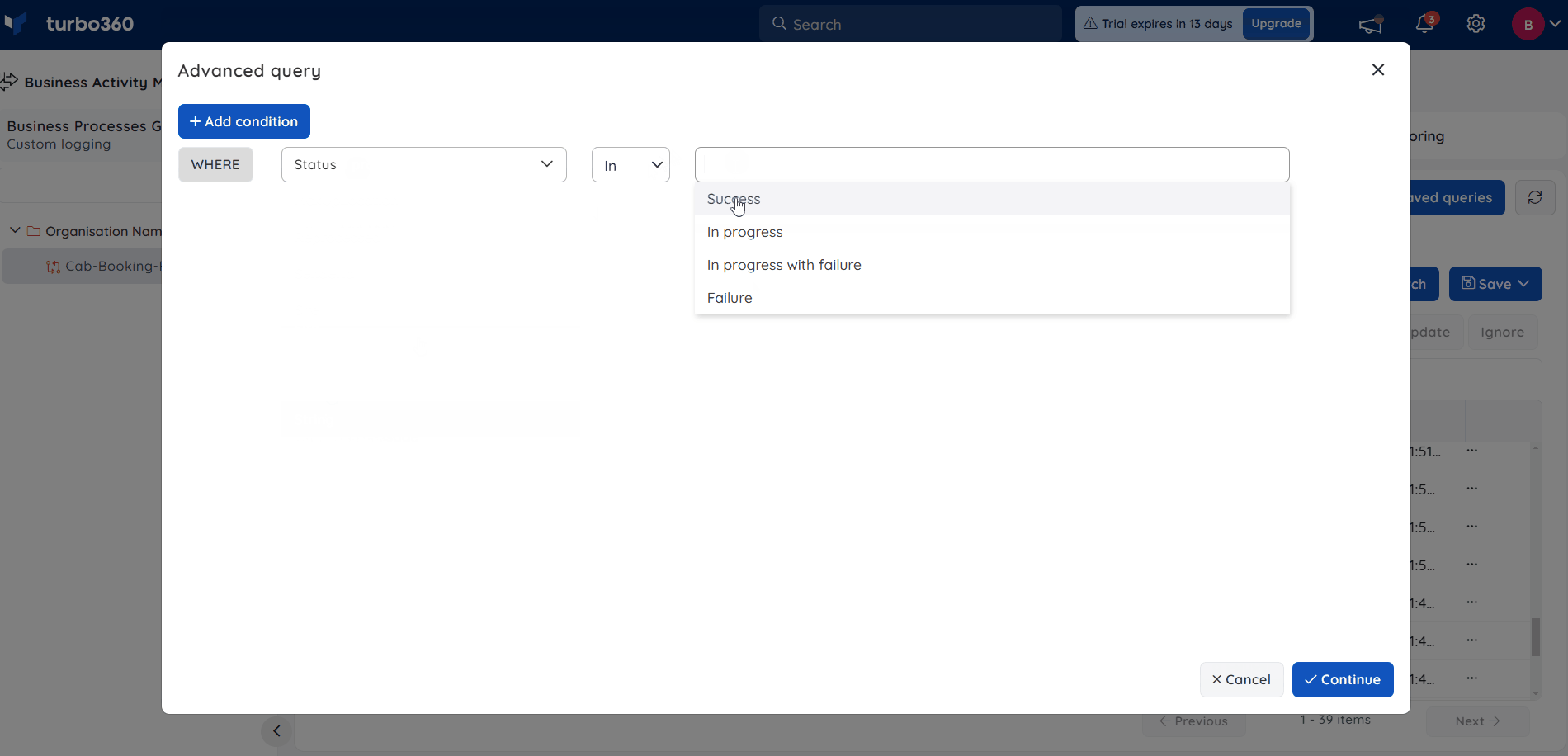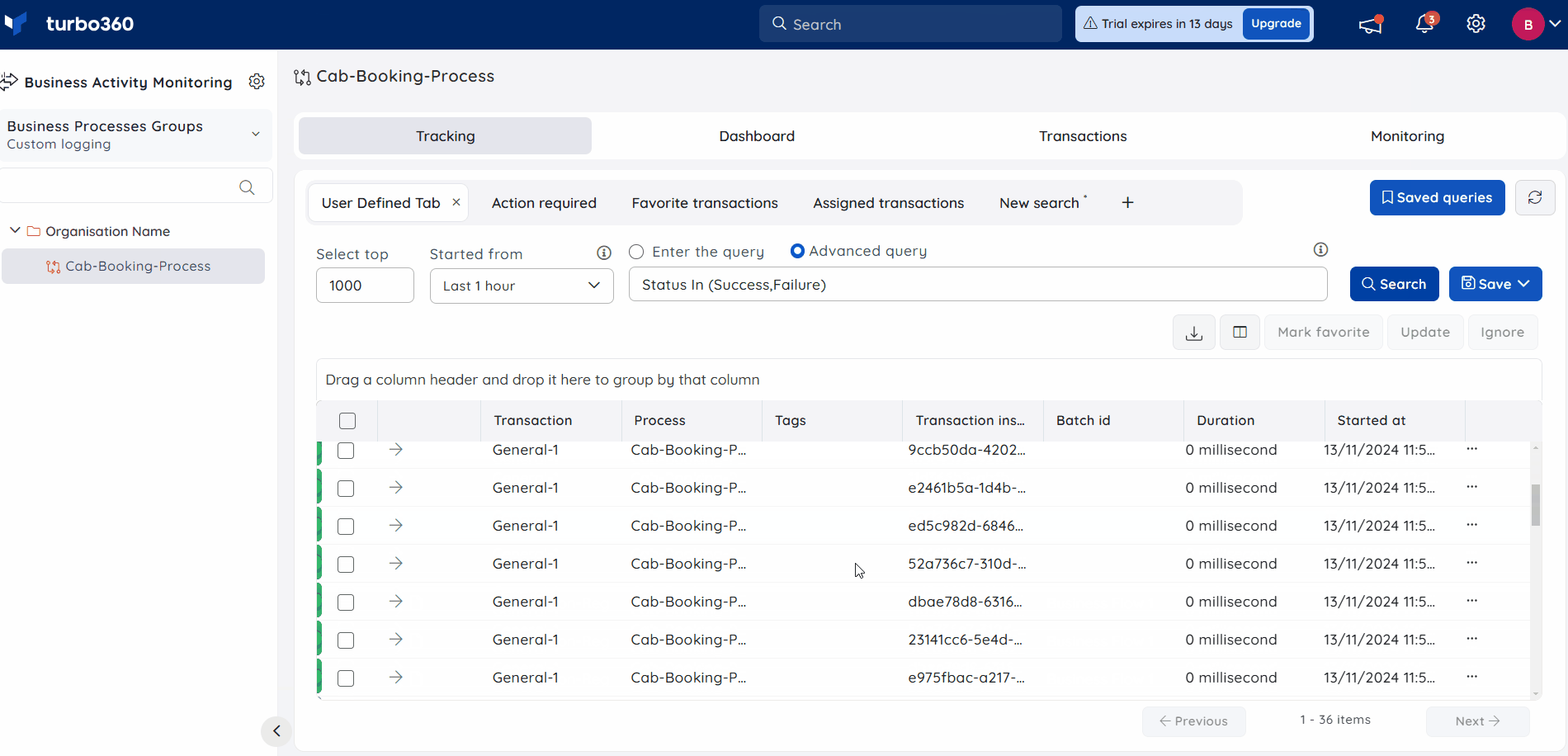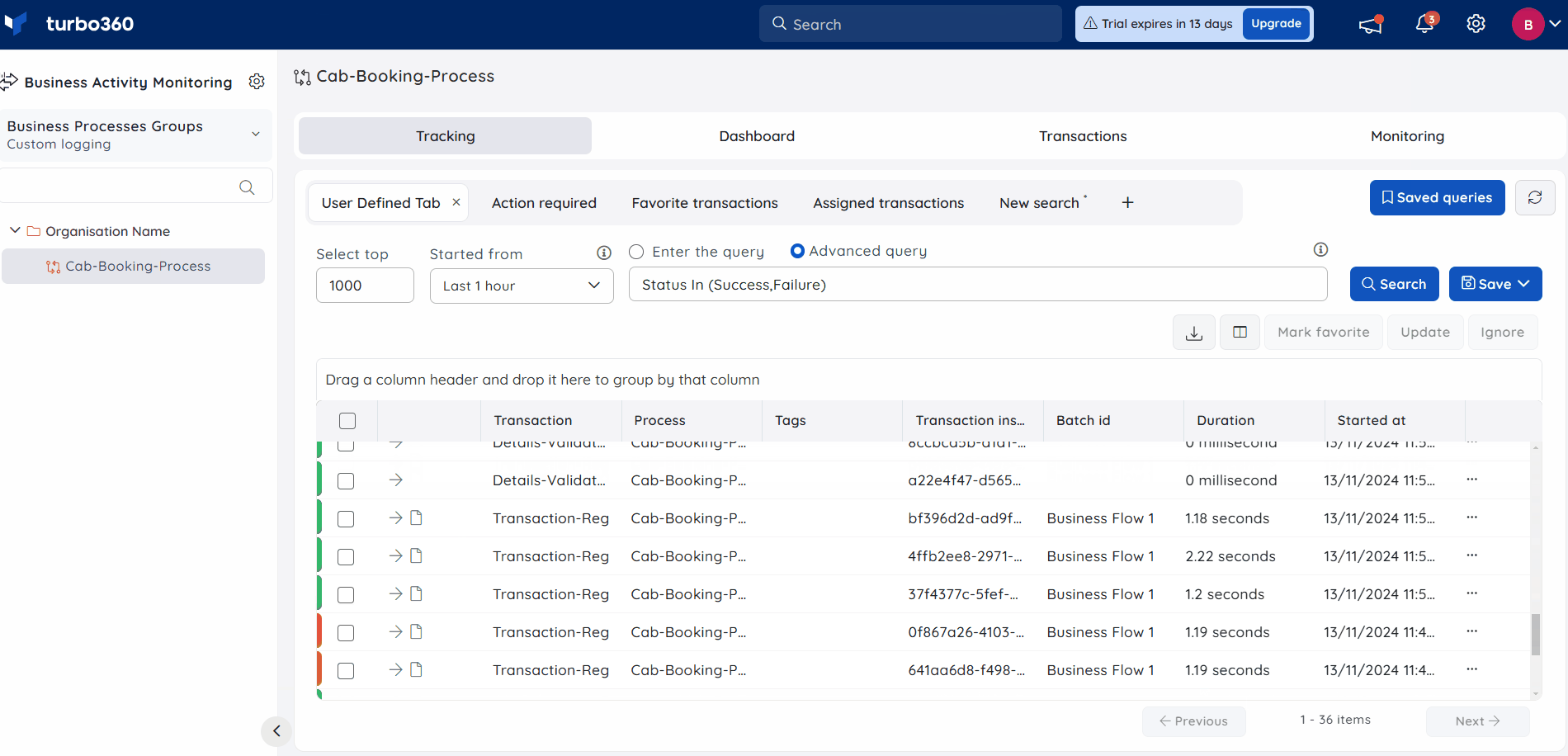
Advanced Query
Advanced query support is available only in the Custom Logging type.
Creating a query to search across multiple values for properties is a time-consuming process, and advanced queries are typically used in such cases.
E.g., Suppose you have many tracked properties named BookingID, BookingStatus, etc., and the given set of values for it is huge. You can perform advanced query searches by simply choosing the properties and entering the value with the following delimiters (comma, tab, new line).
- Comma separated - value1, value2, value3
- Tab-separated - value1 value2 value3
- New line -
value1
value2
value3
- Input values must be separated by commas (or) tab spaces (or) new lines.
- Multiple conditions can be added for Advanced query search based on SQL operators.
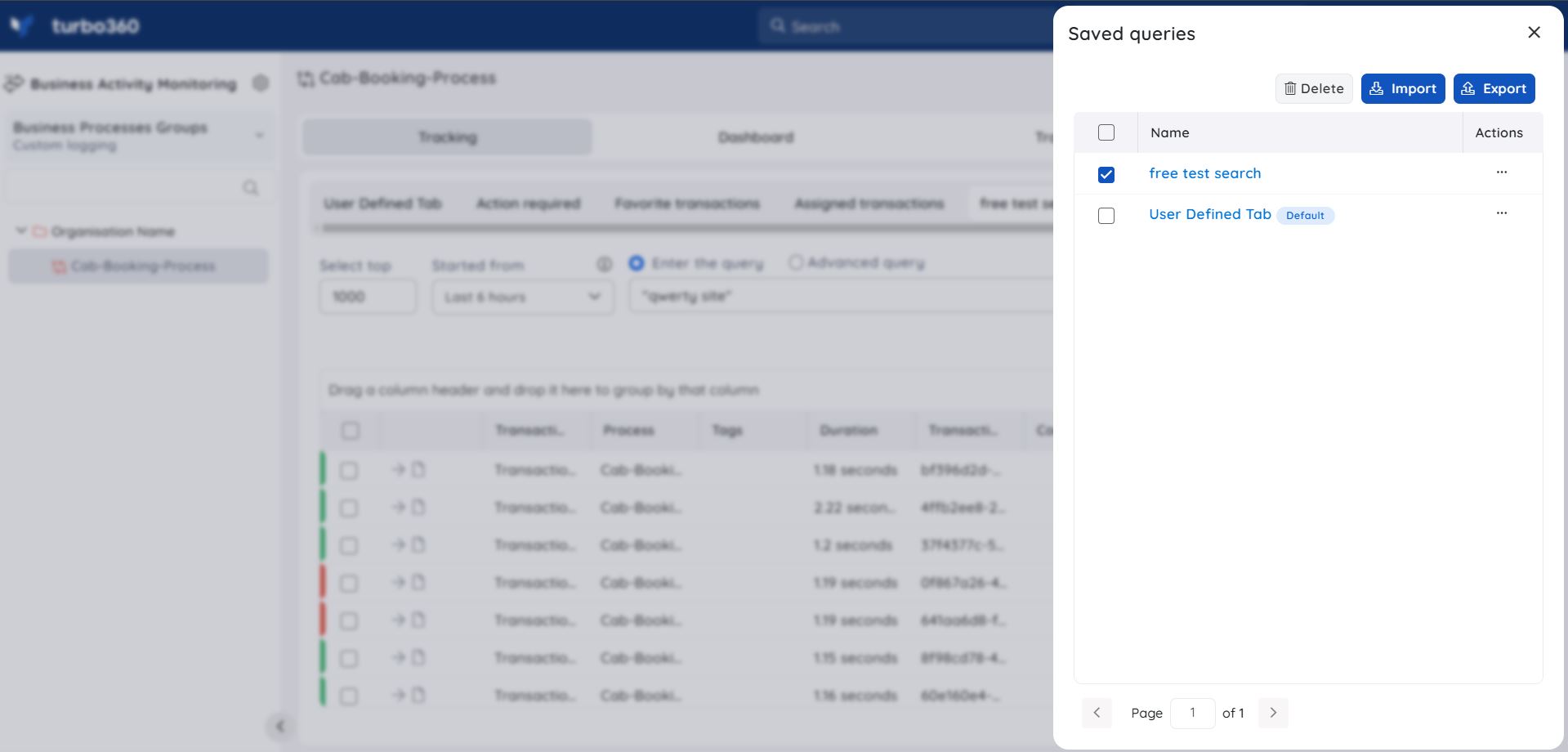
Save a Query
- Provide a query search for a specified time period and then click the Save button once the query data is generated
- Enter a name for the query and click Save
Users can find their saved queries using the Saved queries option available at the top.
The user is also given a checkbox in the Save search blade to set the Query as default.
Import / Export a Query
Users can import queries from any of the downloaded Query files in JSON format with the help of the Import button in the Saved queries blade.
The saved queries can also be exported as a JSON file with the help of the Export button present in the Saved queries blade.
If the user does not provide a name, the query will be given an auto-generated name using time and date data.
Locked Queries
Users can lock saved queries with the help of the Lock option present in the Actions of the Saved queries blade. If a saved query is locked, no other actions can be performed upon the query until the lock is released, thus disabling edit and delete operations on this query.
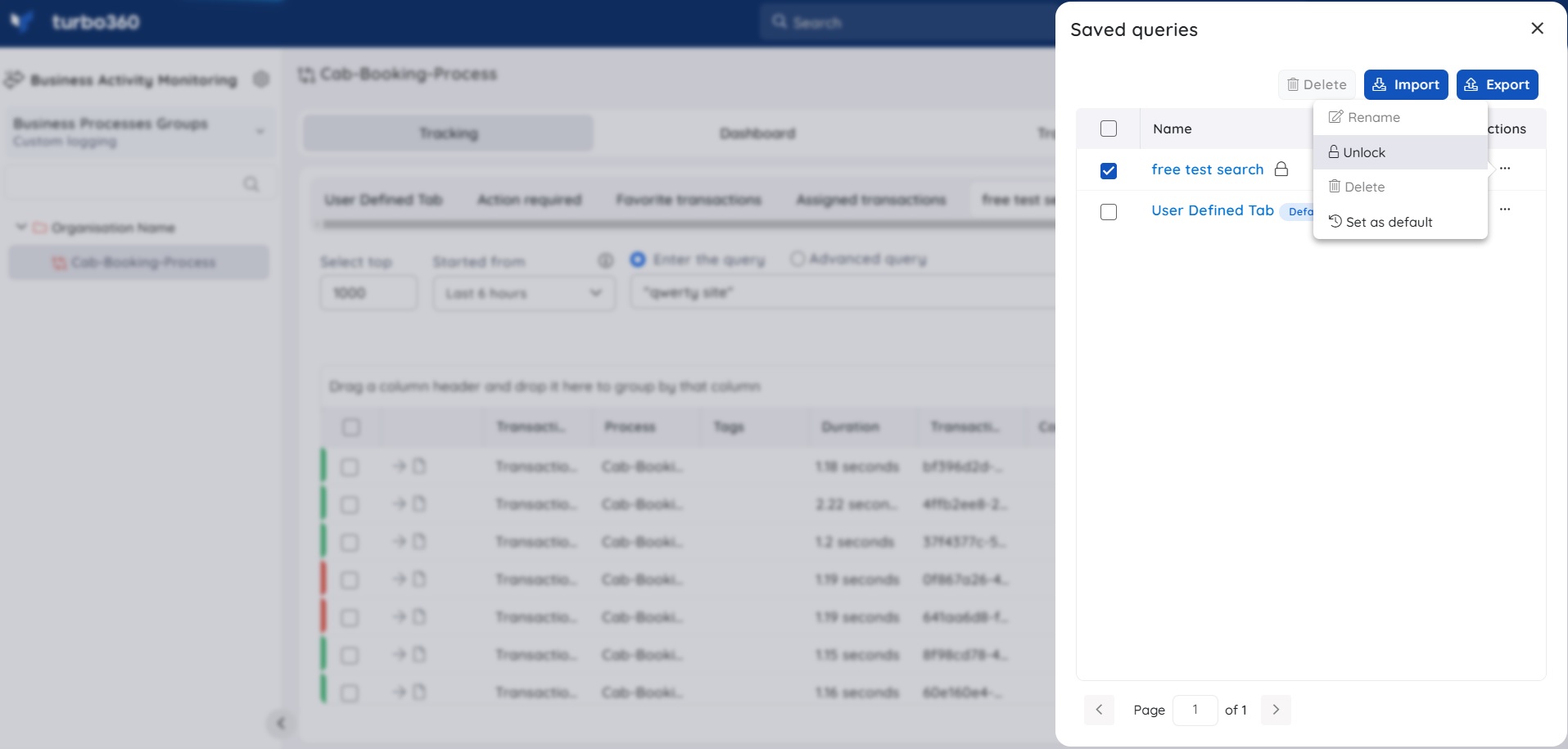
- Users can lock and unlock a saved query with Manage saved queries permission.
- A saved query can be unlocked by the user who locked it or by the users with permission Owner and Account owner.
Data Queries type
Query data available for execution will be sourced from the query defined for a particular transaction during the creation process.
Query language
- Users can query only for the columns available in the Transaction query data using where statements like:
{{column name} {condition} {value}}
- Advanced search options, such as searching for assigned transactions, global properties, the use of wildcard characters, and other features discussed for the Custom Logging query type, will not be available in the Data Queries search type.
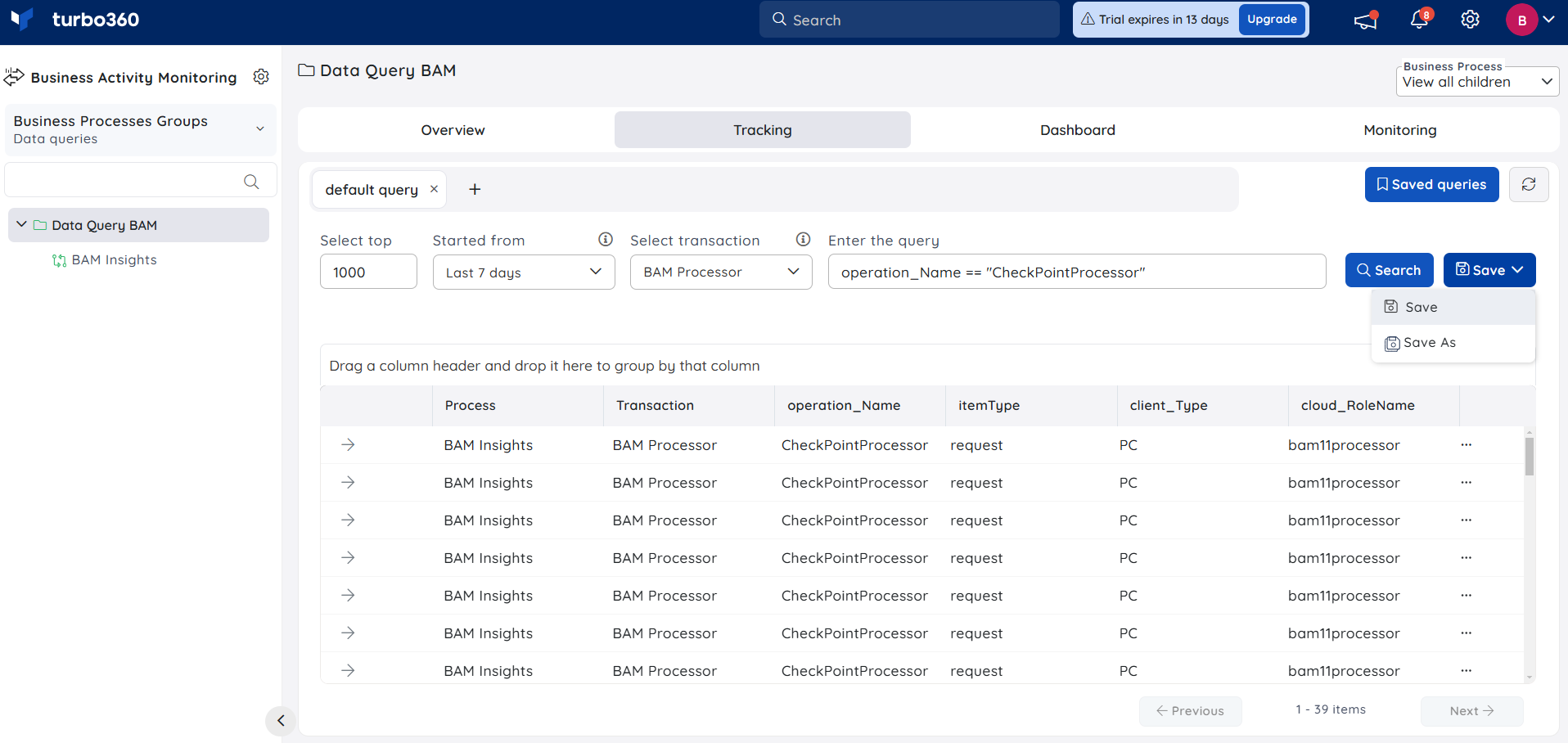
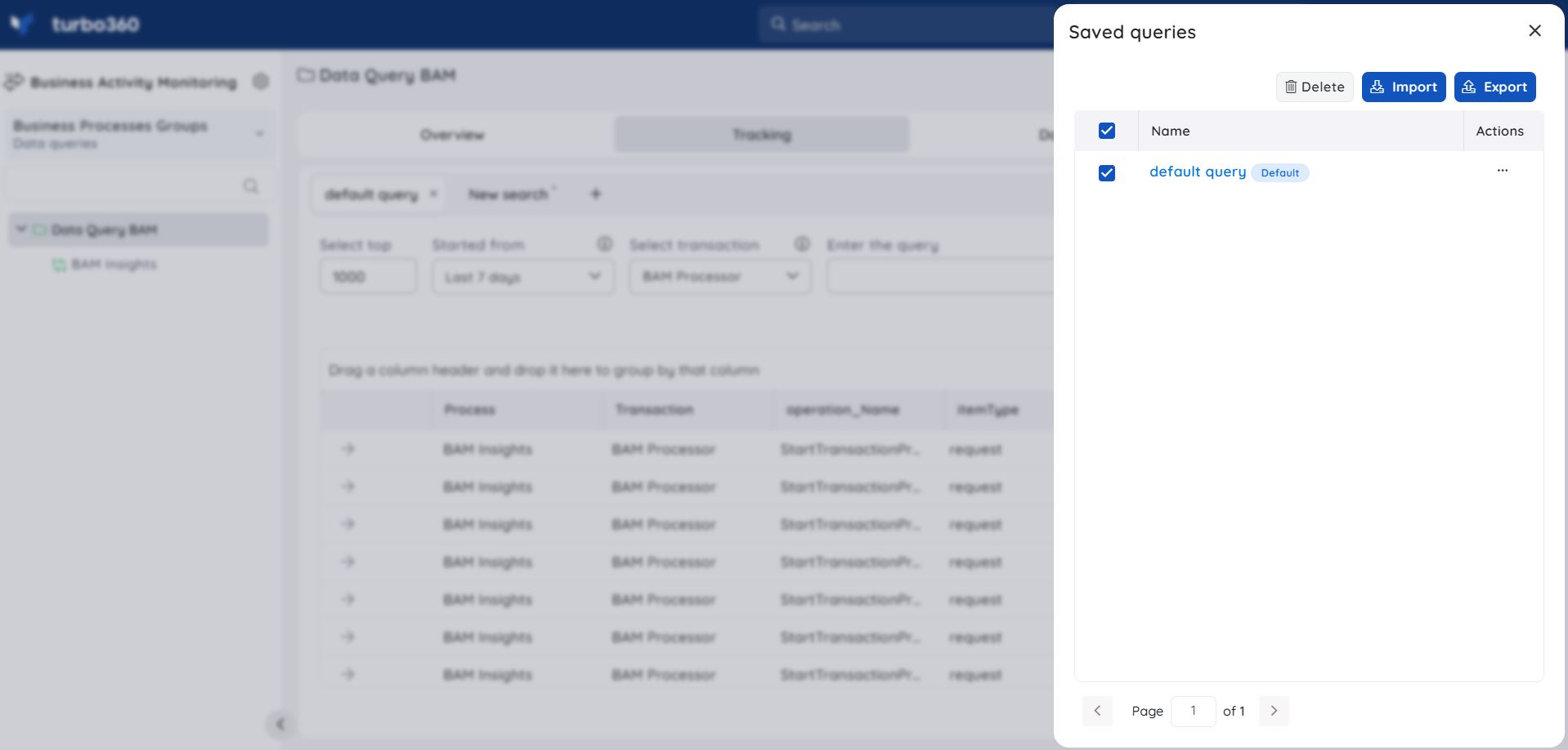
Save a Query
- Provide a query search for a specified time period and then click the Save button once the query data is generated
- Enter a name for the query and click Save
Users can find their saved queries using the Saved queries option available at the top. The user is also given a checkbox in the Save search blade to set the Query as default.{height="" width=""}
Import / Export a Query
Users can import queries from any of the downloaded Query files in JSON format with the help of the Import button in the Saved queries blade.
The saved queries can also be exported as a JSON file with the help of the Export button present in the Saved queries blade.
If the user does not provide a name, the query will be given an auto-generated name using time and date data.
Locked Queries
Users can lock saved queries with the help of the Lock option present in the Actions of the Saved queries blade. If a saved query is locked, no other actions can be performed upon the query until the lock is released, thus disabling edit and delete operations on this query.
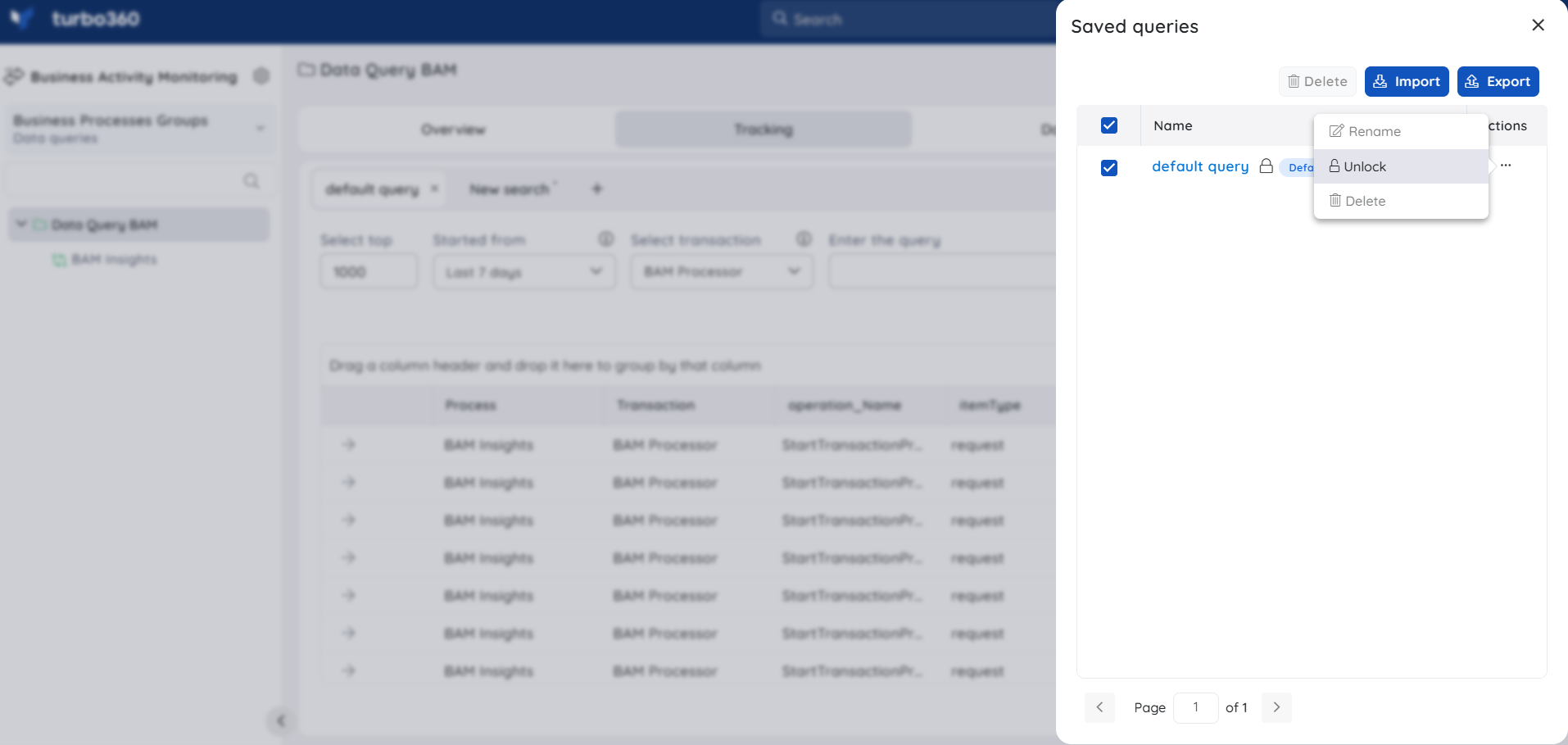
- Users can lock and unlock a saved query with Manage saved queries permission.
- A saved query can be unlocked by the user who locked it or by the users with permission Owner and Account owner.