- 26 Sep 2025
- 4 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Roles and Permissions
- Updated on 26 Sep 2025
- 4 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Introduction
An organization can contain any number of employees or external contractors as users of its Turbo360 account to manage and monitor the associated services.
Not all employees or contractors of an organization can be granted authorization to execute all activities on Turbo360-managed applications. Depending on the features and configurations of the applications, an organization may require many access restrictions. An account with too many permissions is vulnerable to security breaches.
Turbo360's fine-grained access control is aided by a user access policy with personalized function capability.
The first user who signs up for Turbo360 will be given the role of Account Owner, which grants them full access to the account. That user can add an unlimited number of users to Business Activity Monitoring (hereafter referred to as "module") and assign them any system or user-defined roles.
This article explains role management in Business Activity Monitoring. To view role management in other modules of Turbo360, please navigate to the articles given below:
Managing roles
System-defined roles
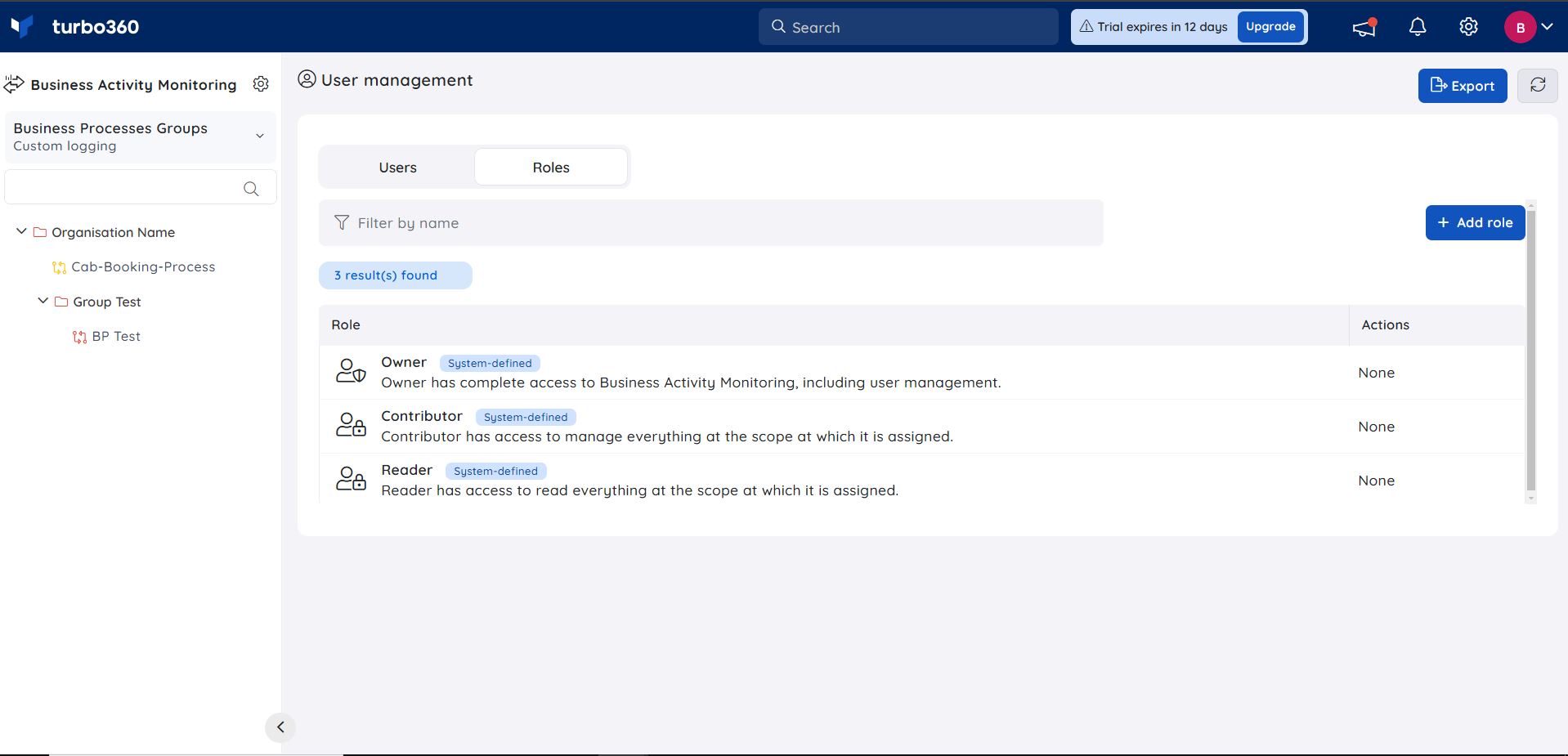
Business Activity Monitoring (hereafter referred to as "module") has three system-defined roles and can contain any number of user-defined roles. The System-defined roles are:
1) Owner
2) Contributor
3) Reader
The Owner has complete access to the module, including managing users and roles in that module. No other role other than Account owner and Owner of the module can manage users and roles.
The Contributor has access to manage everything at the scope at which it is assigned.
The Reader has access to read everything at the scope at which it is assigned.
What is Scope?
The scope of a role determines at which level in the module, a user has permissions that are specified for that role. The scope of a role in Business Activity Monitoring can be any of the two levels given below:
1. Entire module
2. Business Process group
3. Business Process
The below screenshot shows the list of users having access to a Business Process Cab Booking Process.
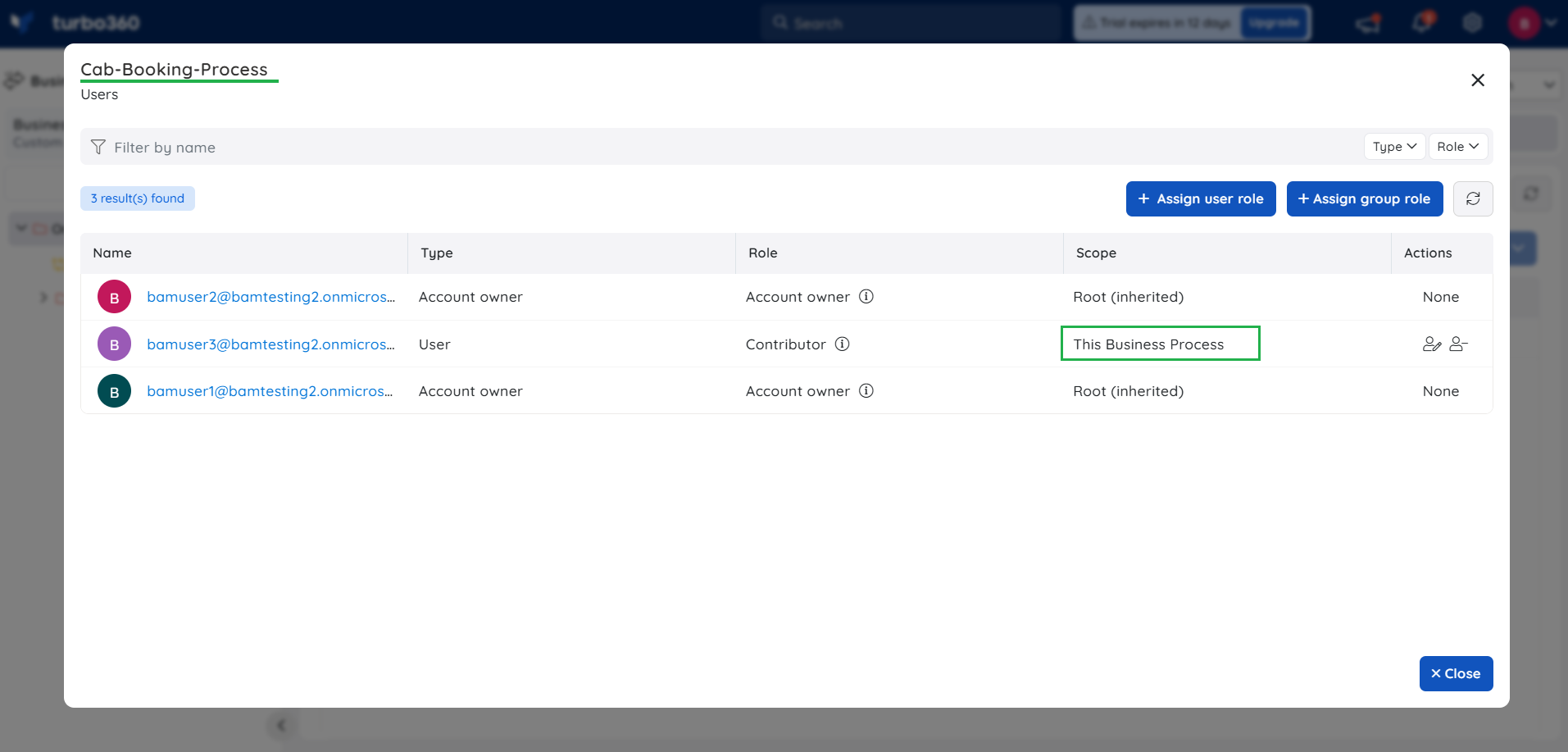
From the Scope column in the screenshot above, it is clear that the first user has got access to this application because that user is an account owner (Having complete access to Turbo360). The second user has got access to this application because that AD group is provided with Contributor access.
User-defined roles
Account owners and owners of the module can add any number of roles to the module. A user-defined role is used to specify permissions in the context of the Business Process. In simple terms, it determines who can do what in a Business Process.
A user-defined role contains two set of permissions: Management permissions and Feature permissions.
Management permissions comprises of the user management permission that allows users to manage users and their permissions. The role creator can choose if this role can contain either read-only or manage permission on user management.
Feature permissions comprises of a set of Business Activity Monitoring features such as Dashboard, Monitoring, Transactions management, and Tracking management. The role creator can choose if this role can contain either read-only or manage permission on these features.
For example, if a group of users needs to configure monitor settings and monitor the Business Processes, and should be restricted from performing other operations that the features of a Business Process provides, then a role can be created with manage permissions only to features related to monitoring, and can be assigned to those users.
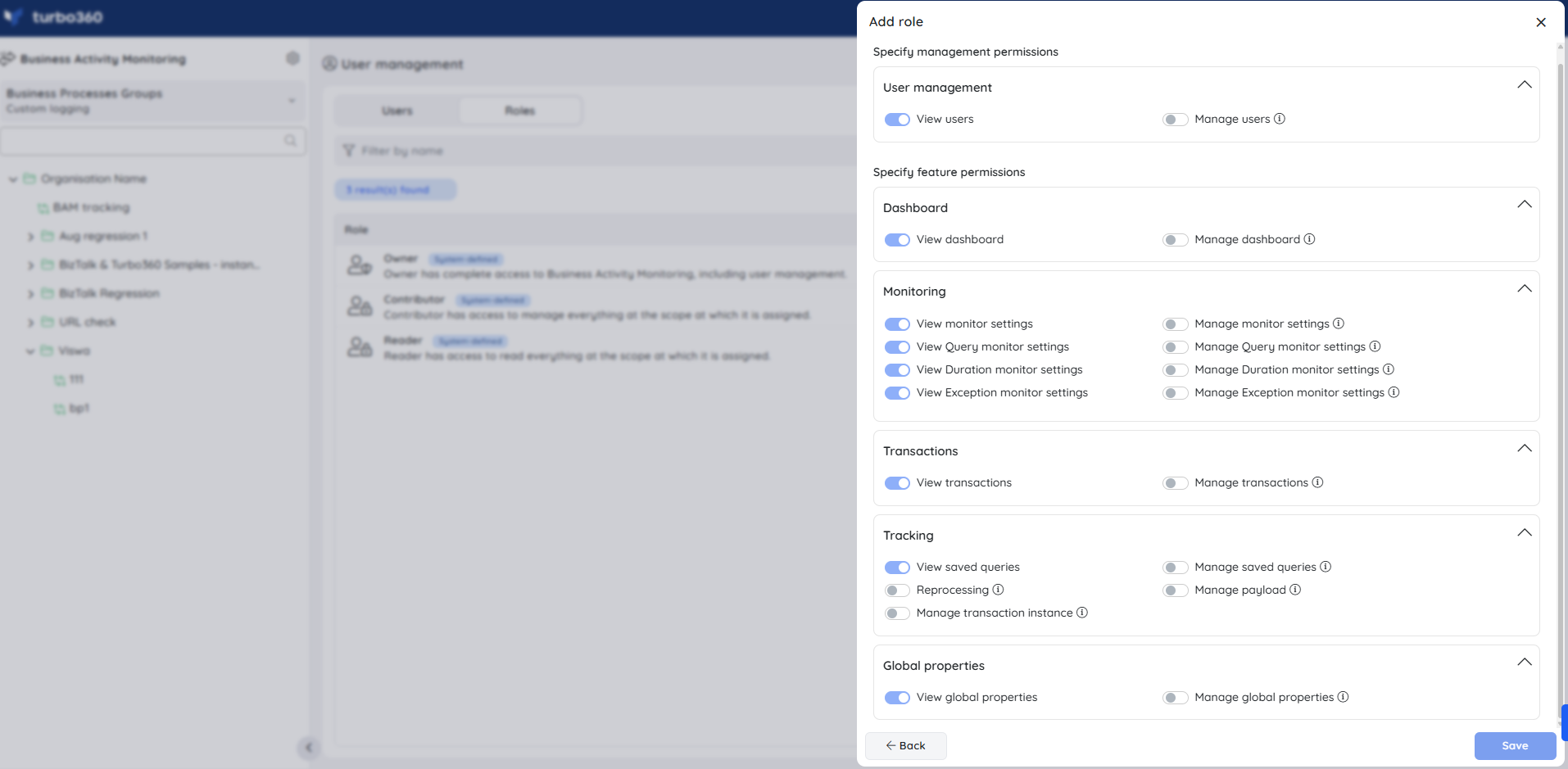
A role can be added by selecting Add role option under the Roles tab. A role must include a name and an optional description, followed by feature permissions.
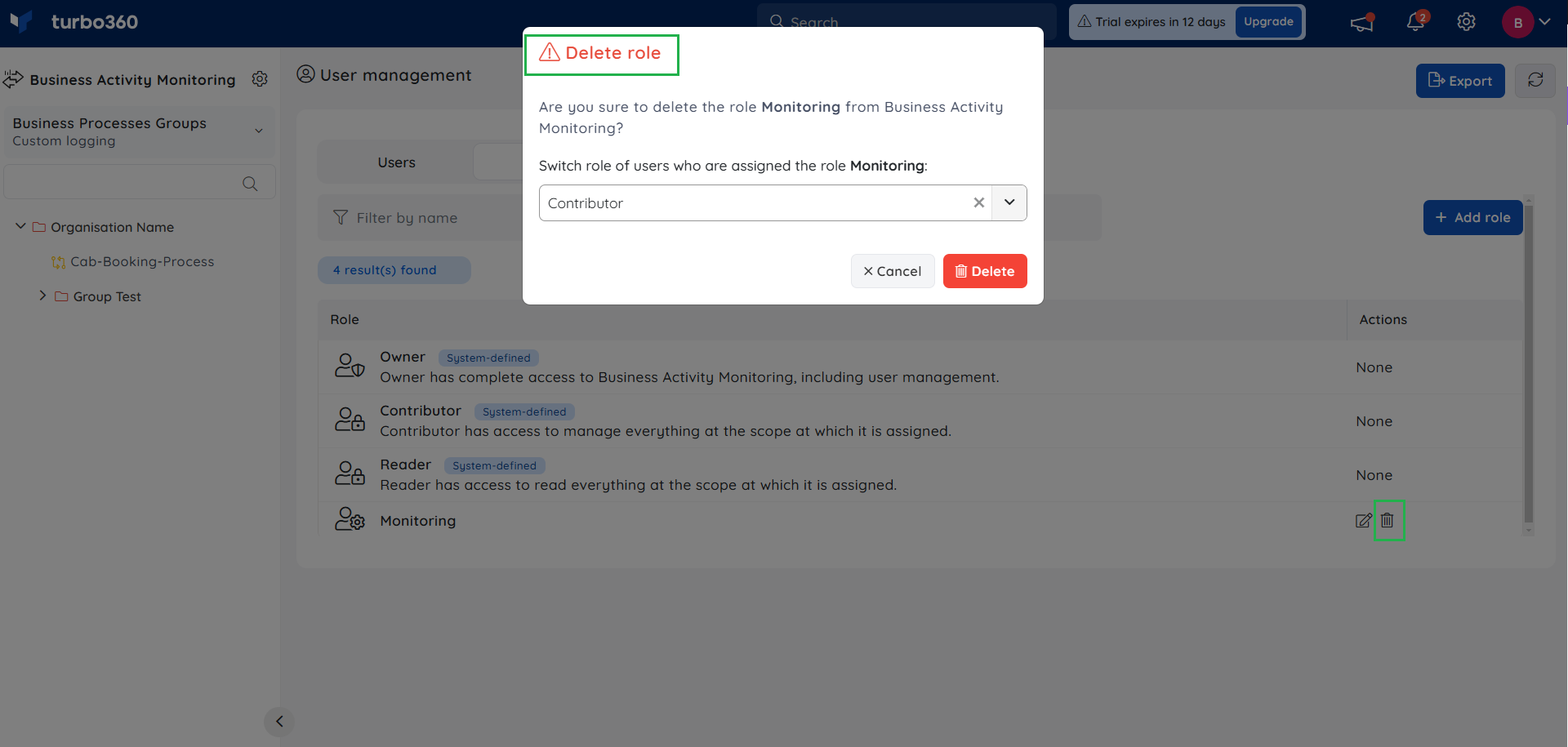
- A user-defined role can be removed any time by clicking the Delete role option in the Actions column under Roles tab. Before deleting, a replacement role must be provided to replace the role of all the users who have been assigned the role that is about to be deleted. As a result, users won't lose access to the module at any scope to which the previous role was assigned.
System vs User-defined roles
As mentioned above, user-defined roles are used to specify permissions in the context of the Business Process. Performing operations on top of a Business Process, such as editing/deleting the Business Process, updating BAM storage details or service principal details, managing global properties, deploying custom connectors requires at least a Contributor role.
For example, if a user is a good fit for managing a Business Process set up for testing but not for managing a Business Process set up for production, that user can be assigned a Contributor role for testing Business Process and any other suitable role with restricted permissions for production. If a user is a good fit for managing the entire BAM configuration and setup in Turbo360 (for example, a team lead), but not for managing users and their roles, that user can be assigned a Contributor role across the product.
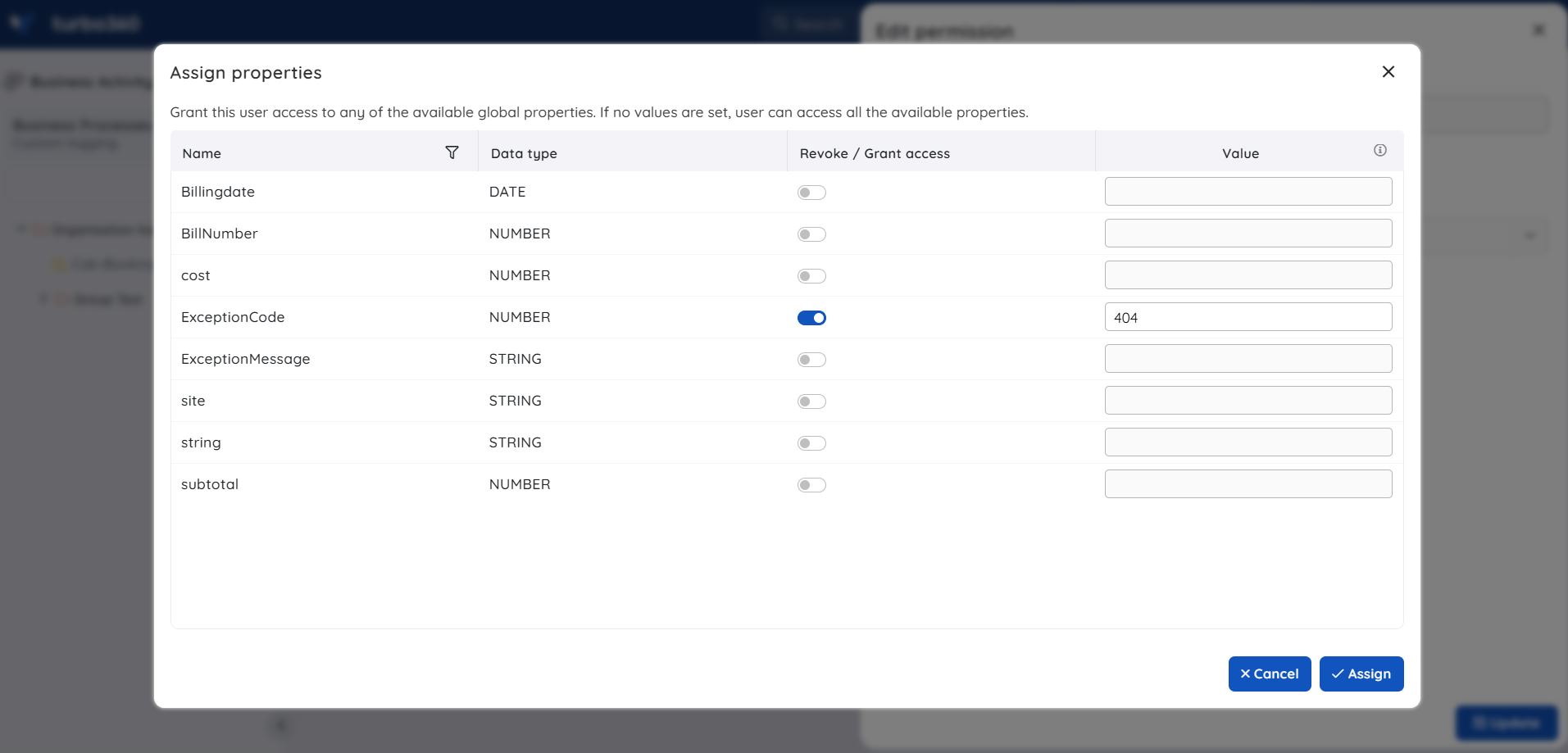
Access policy for global property
The account owner can restrict the user access based on the global properties.
Users will only have access to the transaction instances that contains the global properties configured for them.
The global property permissions can be configured by clicking Configure option while granting specified permissions to a user.
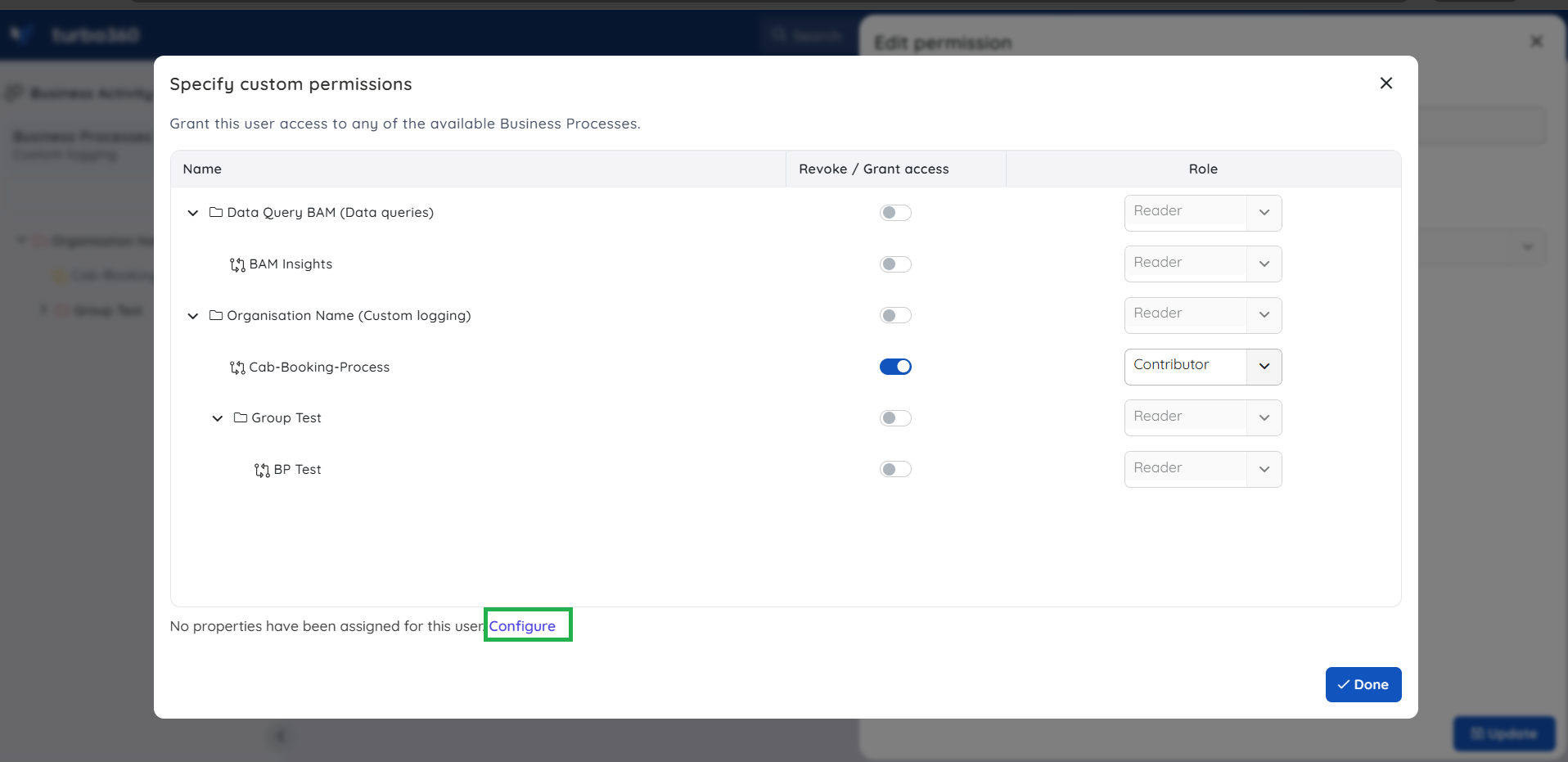
- A global property can be configured with multiple values.
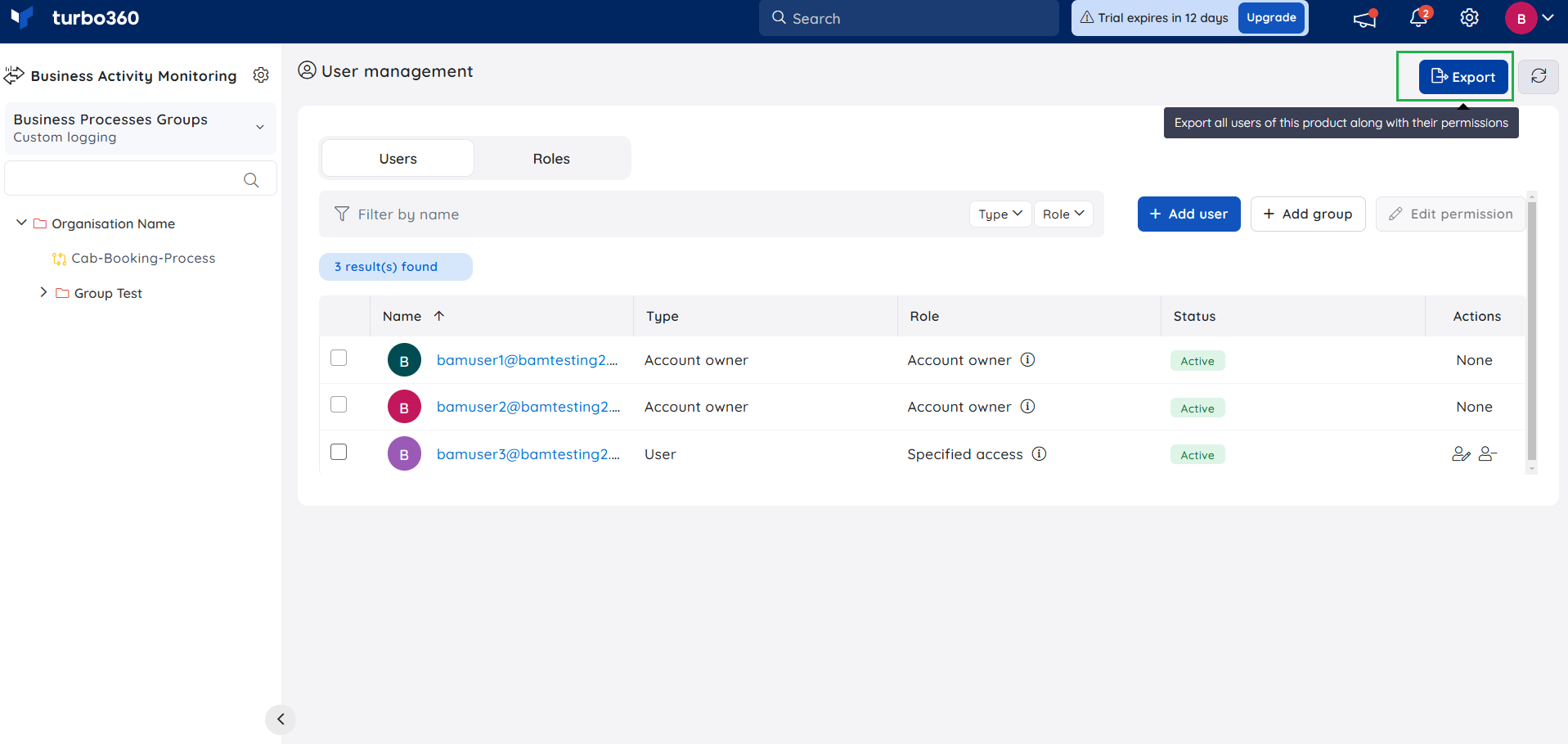
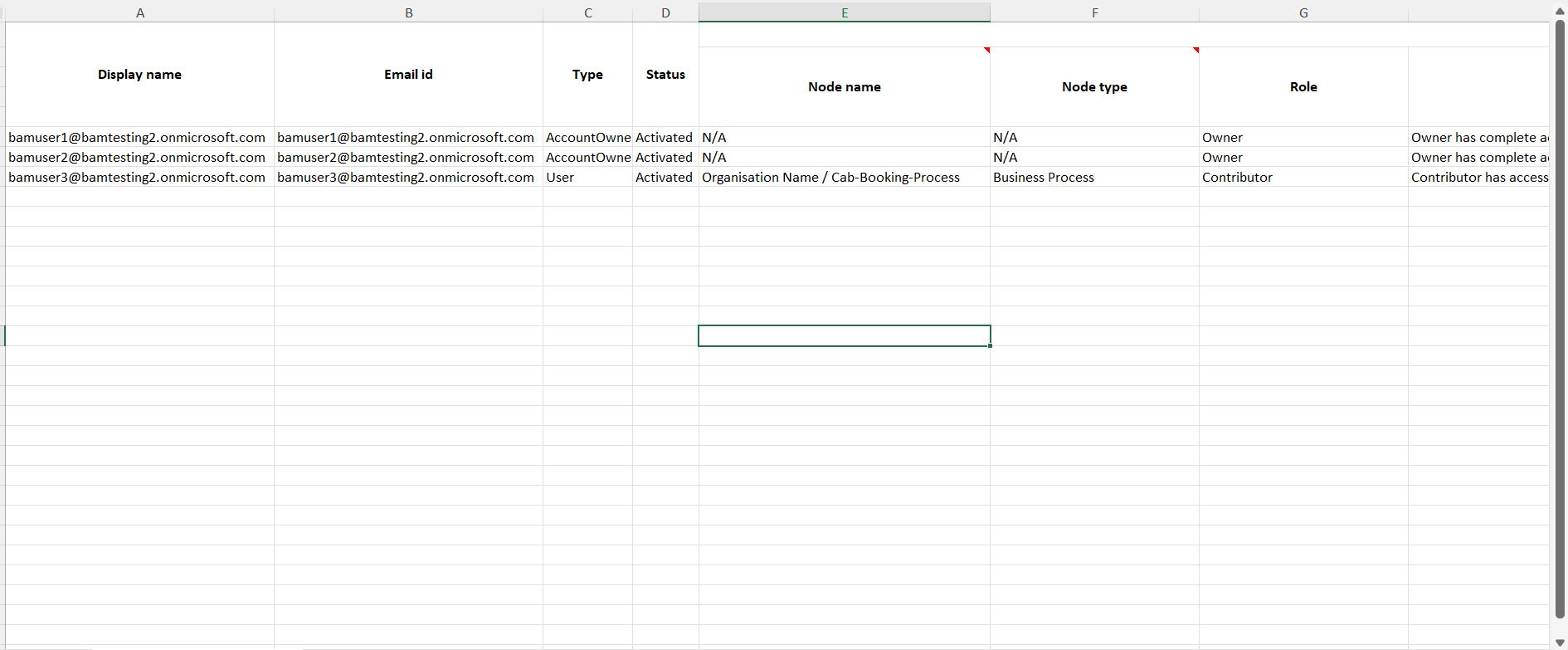
Export user details with permissions
Users can export Turbo360 account details, along with their user permissions, in a CSV format, which allows them to view the permissions provided to each user at various levels within the account.